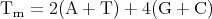
The melting temperature of a specific oligonucleotide primer (Tm) can be calculated by several different ways. The used primer pairs should be constructed to have a similar Tm. The simplest equation, often used, is
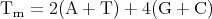
where A, C, G, and T symbolise the count of the particular nucleotide in the primer. This formula was developed for hybridisation assays with oligonucleotides at a salt concentration of 1 M [128]. The equation is inaccurate for calculation of Tm of primers longer than 20 nt. Usually, the chosen annealing temperature is about 5℃C below the calculated Tm and is determined by trial and error.
Other equations used are
![T = 81.5 + 16.6(log[J+]) + 0.41(%G + C) - (600∕l)
m(gc)](start_html7x.png)
where J+ is the concentration of monovalenced cations and l is the length of the oligonucleotide [129]. This formula is correct for oligonucleotides with a length between 14 and 70 nucleotides.
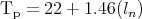
This formula calculates Tp, the optimal annealing temperature ± 2–5℃C. ln is the effective length of the primer: 2G + C) + (A + T) [130]. This equation should result in correct values for oligonucleotides with 20 to 35 nucleotides.
© 2001 Alexander Binder